
This post was written by Tim Johnston, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP, clinical pharmacy specialist in Internal Medicine & Neurology.
Information overload
The amount of information on COVID-19 is overwhelming, to put it mildly, and growing every second. Similarly, the amount of information on vitamins has also grown dramatically. A simple internet search for “vitamin covid” yields half a billion results! It’s no wonder so many are struggling with the best strategies for managing their health. Here, I provide a short review of vitamins and their role in preventing or treating COVID-19.
The big picture: Vitamins
There are 13 vitamins – A, C, D, E, K and 8 different B vitamins (B1, B2, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12). These are all necessary for human life, but our bodies cannot make them. We must get them in our diet or as a supplement to live. Vitamins support many bodily functions such as fighting infection, blood clotting/thinning balance and metabolic energy use. It’s important to know that too much of nearly any vitamin can be dangerous, even deadly.
The big picture: COVID-19
Some viruses are mild in their effect, but COVID-19 (caused by a corona virus) can have severe effects. The most well-known effects are oxygen transport disruption, abnormal blood clotting, and inflammation “storm.”
The vitamin breakdown
Based on what is known about what COVID-19 can do to our bodies, and the potential for vitamins to help or protect them, there has been much said and written about how supplements could be beneficial. Let’s look at some of these suggestions.
- Vitamin A has a role in the immune system, but has not been studied for COVID-19 relief or prevention.
- We know that patients who have a vitamin B1, also known as thiamine deficiency, do worse when critically ill, but no specific benefit has been found through supplementation for COVID-19 patients.
- Vitamins B2 (riboflavin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine) B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cyanocobalamin) have many roles in metabolic processes, but none of these have been studied in treatment or prevention of COVID-19.
- Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is known for roles in fighting infection and reducing inflammation. It is the best studied vitamin in patients who have COVID-19, however, none of these vitamin C studies have shown benefit for COVID-19 patients.
- Vitamin D also has a role in fighting infections. Some have speculated a link between COVID severity and vitamin D deficiency, but no study has shown that Vitamin D benefits COVID-19 patients.
- Vitamin E has a significant role in the immune system but has not been shown to benefit COVID-19 patients.
- Vitamin K is important for maintaining blood clotting/thinning balance. One study showed that COVID-19 patients with vitamin K deficiency did have worse outcomes. There is no study yet showing benefit from supplementing vitamin K for COVID-19 patients. Please note: Patients on some blood thinners should not start any form of vitamin K without their doctor’s permission.
What do we do with all this information?
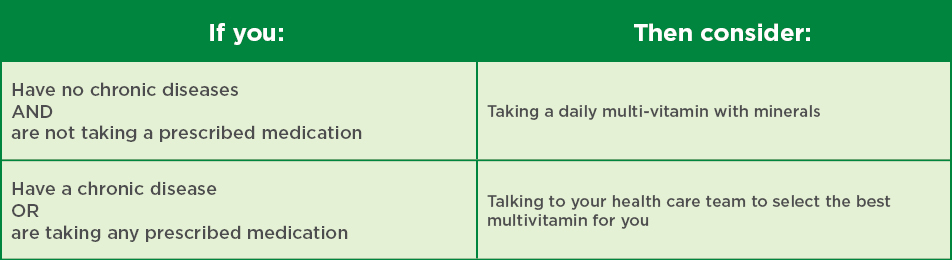
The big takeaway is that vitamins may help, but there just isn’t any evidence as to which ones or how much of them could be used for the treatment or prevention of COVID-19. If you are interested in beginning or adjusting your supplementation regimen, reach out to your primary care provider to ask about potentially using a multivitamin with or without minerals.
Sources
https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/vitamins-and-minerals
https://www.ashp.org/-/media/assets/pharmacy-practice/resource-centers/Coronavirus/docs/ASHP-COVID-19-Evidence-Table.ashx
https://www.endocrine.org/news-and-advocacy/news-room/2020/joint-guidance-on-vitamin-d
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Vitamina-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/riboflavin-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/biotin-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/folate-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Vitaminc-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Vitamind-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Vitamine-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Vitamink-HealthProfessional/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7161532/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341725935_Reduced_Vitamin_K_Status_as_A_Potentially_Modifiable_Prognostic_Risk_Factor_in_COVID-19